

Oxygen saturation as measured by pulse oximetry Oxygen saturation of the hemoglobin of arterial blood The term formerly used ( A-a D O 2) is discouraged.Īlveolar-arterial tension ratio P aO 2: P AO 2 The term oxygen exchange index describes this ratio.
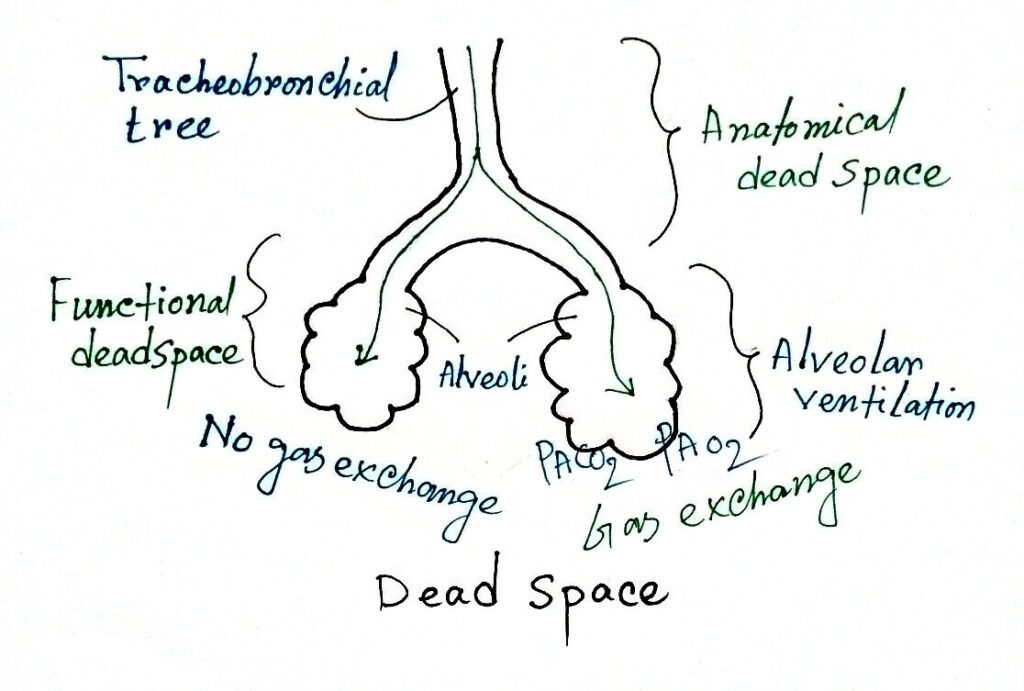
Physiological dead space = Anatomical dead space + Unused ventilated air Figure: Physiological and anatomical dead space The air that is trapped at any point in the respiratory tract that does not participate in the gaseous exchange is called physiological dead space. Normal Value: The volume of anatomical dead space air is usually 150 ml and it is 20-30% of tidal volume (TV).The volume of air that is confined to the transport area of the respiratory tract and does not participate in the exchange of gas is called anatomical dead space. Respiratory dead space is generally two types – Anatomical dead space and Physiological dead space. The part of the respiratory tract where the trapped air does not participate in gaseous exchange is called respiratory dead space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
